# 洋葱模型 和 组合函数 compose
# koa2 使用 async/await + koa-compose 来实现洋葱模型
附:经典图,表明请求与响应时中级件的执行顺序
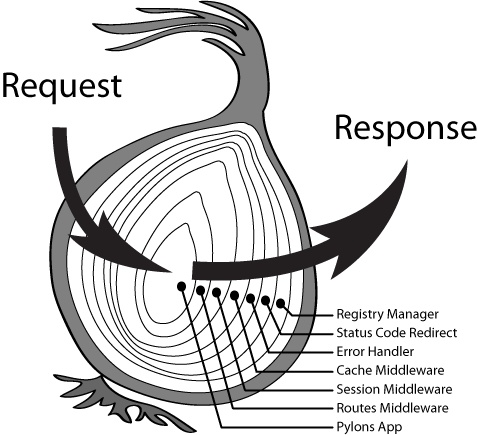
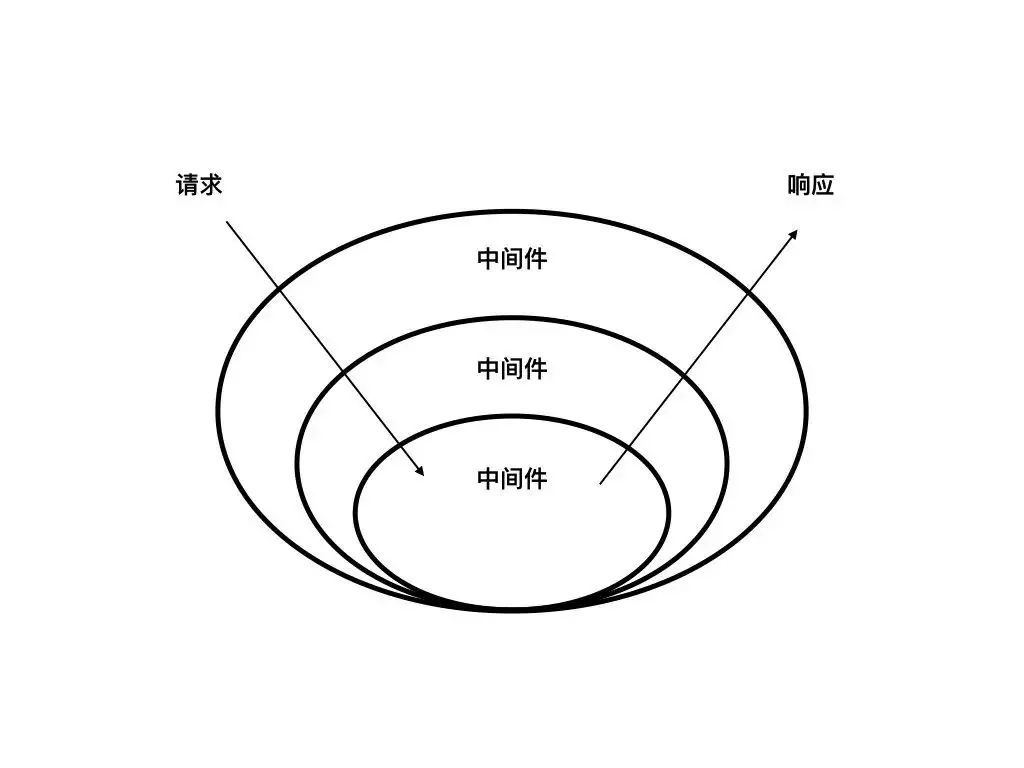
# 洋葱模型案列 - koa
const Koa = require("koa");
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
console.log("no.1中间件:1");
await next(); // 执行下一个中间件
console.log("no.1中间件:2");
});
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
console.log("no.2中间件:3");
await next(); // 执行下一个中间件
console.log("no.2中间件:4");
});
// response
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
console.log("no.3中间件:5");
await next(); // 执行下一个中间件
console.log("no.3中间件:6");
});
app.listen(3000);
// 执行结果
// no.1中间件:1
// no.2中间件:3
// no.3中间件:5
// no.3中间件:6
// no.2中间件:4
// no.1中间件:2
# 如何通过 koa-compose 来实现的
//koa-compose 源码
function compose(middleware) {
if (!Array.isArray(middleware))
throw new TypeError("Middleware stack must be an array!");
for (const fn of middleware) {
if (typeof fn !== "function")
throw new TypeError("Middleware must be composed of functions!");
}
/**
* @param {Object} context
* @return {Promise}
* @api public
*/
return function (context, next) {
// last called middleware #
let index = -1;
return dispatch(0);
function dispatch(i) {
if (i <= index)
return Promise.reject(new Error("next() called multiple times"));
index = i;
let fn = middleware[i];
if (i === middleware.length) fn = next;
if (!fn) return Promise.resolve();
try {
return Promise.resolve(fn(context, dispatch.bind(null, i + 1)));
} catch (err) {
return Promise.reject(err);
}
}
};
}
# compose 组合函数案列 - lodash > flowRight
function flow(...funcs) {
const length = funcs.length;
let index = length;
while (index--) {
if (typeof funcs[index] !== "function") {
throw new TypeError("Expected a function");
}
}
return function (...args) {
let index = 0;
let result = length ? funcs[index].apply(this, args) : args[0];
while (++index < length) {
result = funcs[index].call(this, result);
}
return result;
};
}
function flowRight(...funcs) {
return flow(...funcs.reverse());
}
# compose 组合函数案列 - redux > compose
export default function compose(...funcs: Function[]) {
if (funcs.length === 0) {
// infer the argument type so it is usable in inference down the line
return <T>(arg: T) => arg;
}
if (funcs.length === 1) {
return funcs[0];
}
return funcs.reduce(
(a, b) =>
(...args: any) =>
a(b(...args))
);
}